Psoriasis is a noncontagious skin condition that produces plaques of thickened, scaling skin. The dry flakes of skin scales result from the excessively rapid proliferation of skin cells. The proliferation of skin cells is triggered by inflammatory chemicals produced by specialized white blood cells called lymphocytes.
Types of psoriasis

There are different types of psoriasis. Some affect only skin while others affect other vital organs of the body like eyes, oral cavity, nails and joints.
- Psoriasis vulgaris is the most common type of psoriasis and involves the scalp, extensor surfaces, genitals, umbilicus, trunk and ears.
- Plaque psoriasis is characterized by raised, inflamed lesions covered with silvery white scale.
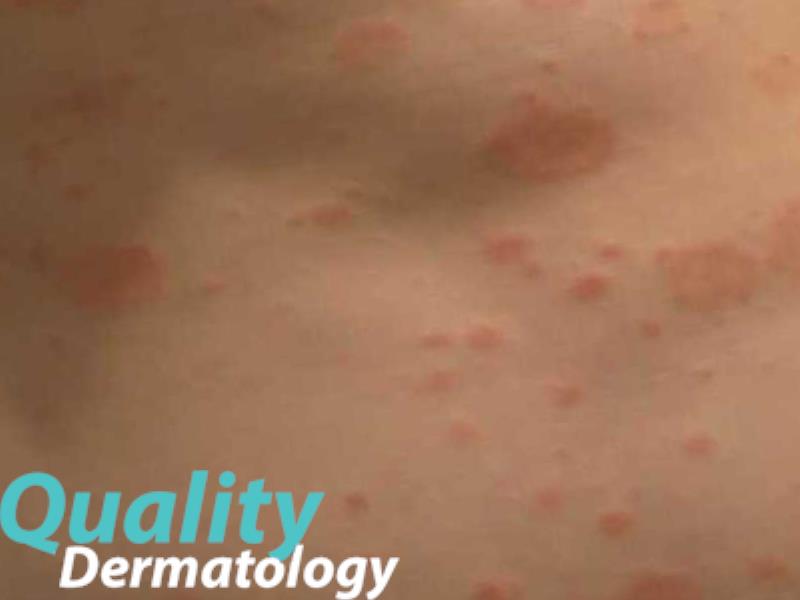
- Guttate psoriasis presents as small salmon-pink papules, 1-10 mm in diameter, predominately on the trunk.
- It frequently appears suddenly, 2-3 weeks after an upper respiratory infection (URI) with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. This form of psoriasis might cause heart complications if not promptly identified and treated.
- Pustular psoriasis presents as pustules appearing on the palms and soles or diffusely over the body.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis presents as generalized erythema, pain, and itching. It typically encompasses nearly the entire body surface area. It may be accompanied by fever, chills, hypothermia and dehydration secondary to the large body surface area involvement.
- Scalp psoriasis affects approximately 50% of patients. It presents as erythematous raised plaques with silvery white scales on the scalp.
- Nail psoriasis may cause pits on the nails, which often become thickened and yellowish in color. Nails may separate from the nail bed. Psoriatic nails may be indistinguishable from fungal nails so your dermatologist can perform certain tests to determine the diagnosis.
- Inverse psoriasis occurs on the flexural surfaces, armpit, groin, under the breast, and in the skin folds. It is characterized by smooth, inflamed lesions without scaling due to the moist nature of the area where this type of psoriasis is located.
- Oral psoriasis may present with whitish lesions on the oral mucosa. Geographic tongue is considered by many to be an oral form of psoriasis.
- Eruptive psoriasis involves the upper trunk and upper extremities. Most often, it is seen in younger patients.
Complications of psoriasis may include the following:
- Secondary infections
- Possible increased risk of lymphoma
- Possible increased risk of cardiovascular and ischemic heart disease
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Mitral valve prolapse
Psoriasis symptoms

Even after plaques have cleared, there may be a longstanding or permanent discoloration. Arthritis, if not controlled, may be mutilating and crippling. It is suggested that psoriatic patients have a higher incidence of cancer, especially lymphoma, but how much of this increased risk can be ascribed to the psoriasis and how much to the medications used for psoriasis is less certain. Psoriatic patients have a higher incidence of depression and anxiety.
Sometimes your dermatologist might need to do a biopsy to confirm psoriasis. Treatment regimens depend on the severity of the condition. It could be topical, oral, injection or a combination of a few. However,inspiteofarangeofoptions, effective treatment of psoriasis can be challenging. The disease is unpredictable, going through cycles of improvement and worsening, seemingly at random. Effects of psoriasis treatments also can be unpredictable; what works well for one person might be ineffective for someone else. Your skin also can become resistant to various treatments over time, and the most potent psoriasis treatments can have serious side effects.
Talk to your dermatologist about your psoriasis and treatments available.
